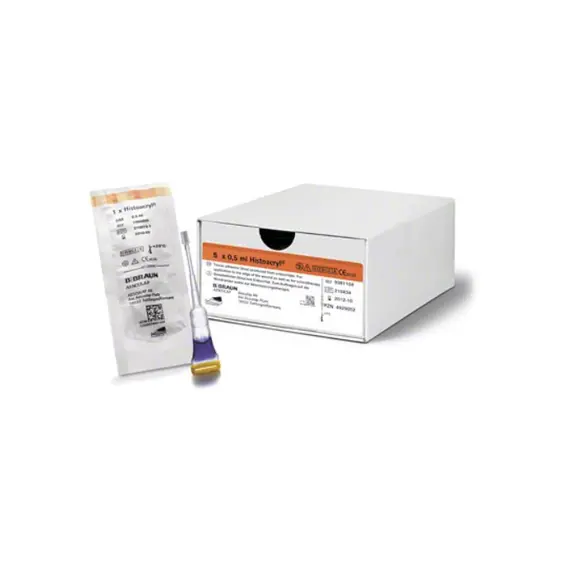
HISTOACRYL ® ( MONOMERIC N-BUTYL-2-CYANOACRYLATE ) 5 X 0.5 ML INJECTIONS
- Fast delivery
- Email notifications
- Different payment methods
- Competitive prices
HISTOACRYL ® ( MONOMERIC N-BUTYL-2-CYANOACRYLATE ) 5 X 0.5 ML INJECTIONS
The tissue adhesive Histoacryl® consists of monomeric n-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate, which polymerises quickly in connection with tissue fluid. Histoacryl® is available in two colours: translucent, special for facial application, and blue, which enables an easy control over the quantity applied in different indications approved.
Advantages Skin closure
Wound closure in one minute [1, 2, 3, 4] Significant less pain than suture materials [5] Effective microbial barrier [6, 7, 8] Storage at room temperature <22º [9] High level of patient and physician satisfaction [2, 7, 10, 11, 12] Save time and costs [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 12] Only one layer is needed [4, 8] Histoacryl® can be used for closure of endoscopic incisions [8, 13]
Sclerotherapy
For bleeding and non-bleeding varices [14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19] Combined therapy with Histoacryl® and conventional sclerosation therapy is possible] [14, 15, 17, 20] Final hemostasis is achieved in >90% of cases [14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19] Lower rebleeding rate than with band ligation [14, 15, 18, 20] Mesh fixation
Non-invasive method reported to be better tolerated by the patient than traditional fixation methods [22, 23, 24, 25, 26] Stand-alone fixation method in different hernia repair techniques [22, 23, 24, 25, 26] Comparable recurrence rate than with traditional fixation methods [23, 24, 25, 26] Low intra- and postoperative morbidity [24, 26] Reduced risk of post-operative chronic pain compared to traditional fixation methods [23, 24, 25, 26] Decreased surgery time compared to traditional fixation methods [23, 25] Good biocompatibility and in vivo tolerance [23, 24, 25, 26, 27] Indication Skin Closure: Closure of skin wounds without tension (including clean surgical incisions and incisions from minimally invasive surgery), and simple, thoroughly cleansed, trauma-induced lacerations. Sclerotherapy: Sclerotherapy of large oesophageal or fundal varices. Mesh fixation: Fixation of hernia meshes, especially in inguinal hernia surgery.
No reviews found